DataFrame & Dataset 的创建
不要刻意区分:DF、DS。DF是一种特殊的DS
1.由range生成Dataset
val numDS = spark.range(5, 100, 5)2.由集合生成Dataset
case class Person(name: String, age: Int, height: Int)
val seq1 = Seq(Person("Jack", 28, 184), Person("Tom", 10, 144), Person("Andy", 16, 165))
val ds1 = spark.createDataset(seq1)3.由集合生成DataFrame
val lst = List(("Jack", 28, 184), ("Tom", 10, 144), ("Andy", 16, 165))
val df1 = spark.createDataFrame(lst).
// 改单个字段名时简便
withColumnRenamed("_1", "name1").
withColumnRenamed("_2", "age1").
withColumnRenamed("_3", "height1")4.RDD 转成 DataFrame
val arr = Array(("Jack", 28, 184), ("Tom", 10, 144), ("Andy",
16, 165))
val rdd1 = sc.makeRDD(arr).map(f=>Row(f._1, f._2, f._3))5.RDD转Dataset
val ds3 = spark.createDataset(rdd2)6.从文件创建DateFrame(以csv文件为例)
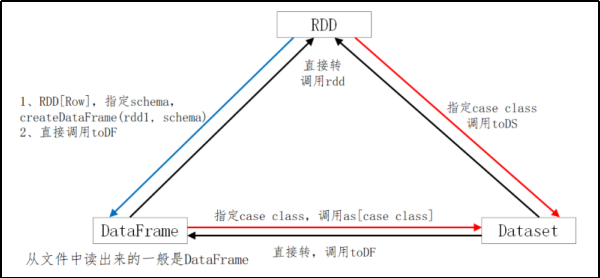
val df2 = spark.read.csv("data/people2.csv")RDD、DataFrame、DataSet三者的转换
Spark SQL 的创建
val df = spark.read.json("examples/src/main/resources/people.json")
df.createOrReplaceTempView("people")
val sqlDF = spark.sql("SELECT * FROM people")
sqlDF.show()Spark SQL 操作详解
查看元数据
spark.catalog.listDatabases()
spark.catalog.listTables()
spark.catalog.listColumns("bigdata_zyy.people")血缘关系通过catalog获取元数据
缓存SQL表
还可以将表声明为 LAZY,这样它就不会立即被缓存,直到第一次使用时才会真正缓存
//缓存表
spark.sql("cache table ds_spark.people")
//清除缓存表
spark.sql("uncache table ds_spark.people")Action操作
与RDD类似的操作
show、 collect、 collectAsList、 head、 first、 count、 take、 takeAsList、 reduce
val df1 = spark.read.
option("header", "true").
option("inferschema","true").
csv("src/main/resources/emp.csv")
df1.count
// 缺省显示20行
df1.union(df1).show()
// 显示2行
df1.show(2)
// 不截断字符
df1.toJSON.show(false)
// 显示10行,不截断字符
df1.toJSON.show(10, false)
spark.catalog.listFunctions.show(10000, false)
// collect返回的是数组, Array[org.apache.spark.sql.Row]
val c1 = df1.collect()
// collectAsList返回的是List, List[org.apache.spark.sql.Row]
val c2 = df1.collectAsList()
// 返回 org.apache.spark.sql.Row
val h1 = df1.head()
val f1 = df1.first()
// 返回 Array[org.apache.spark.sql.Row],长度为3
val h2 = df1.head(3)
val f2 = df1.take(3)
// 返回 List[org.apache.spark.sql.Row],长度为2
val t2 = df1.takeAsList(2)获取结构属性的操作
printSchema、explain、columns、dtypes、col
// 结构属性
df1.columns // 查看列名
df1.dtypes // 查看列名和类型
df1.explain() // 参看执行计划
df1.col("name") // 获取某个列
df1.printSchema // 常用 Transformation 操作
select * from table where ... group by ... having... order by...与RDD类似的操作
map、filter、flatMap、mapPartitions、sample、 randomSplit、 limit、 distinct、dropDuplicates、describe df1.map(row=>row.getAs[Int](0)).show
// randomSplit(与RDD类似,将DF、DS按给定参数分成多份)
val df2 = df1.randomSplit(Array(0.5, 0.6, 0.7))
df2(0).count
df2(1).count
df2(2).count
// 取10行数据生成新的DataSet
val df2 = df1.limit(10)
// distinct,去重
val df2 = df1.union(df1)
df2.distinct.count
// dropDuplicates,按列值去重
df2.dropDuplicates.show
df2.dropDuplicates("mgr", "deptno").show
df2.dropDuplicates("mgr").show
df2.dropDuplicates("deptno").show
// 返回全部列的统计(count、mean、stddev、min、max)
ds1.describe().show
// 返回指定列的统计
ds1.describe("sal").show
ds1.describe("sal", "comm").show存储相关
cacheTable、persist、checkpoint、unpersist、cacheDataset 默认的存储级别是 MEMORY_AND_DISK
import org.apache.spark.storage.StorageLevel
spark.sparkContext.setCheckpointDir("data/checkpoint")
df1.show()
df1.checkpoint()
df1.cache()
df1.persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_ONLY)
df1.count()
df1.unpersist(true)
df1.createOrReplaceTempView("t1")
spark.catalog.cacheTable("t1")
spark.catalog.uncacheTable("t1")select相关
列的多种表示、select、selectExpr
drop、withColumn、withColumnRenamed、cast(内置函数)// 列的多种表示方法。使用""、$""、'、col()、ds("")
// 注意:不要混用;必要时使用spark.implicitis._;并非每个表示在所有的地方都有效
df1.select($"ename", $"hiredate", $"sal").show
df1.select("ename", "hiredate", "sal").show
df1.select('ename, 'hiredate, 'sal).show
df1.select(col("ename"), col("hiredate"), col("sal")).show
df1.select(df1("ename"), df1("hiredate"), df1("sal")).show
// 下面的写法无效,其他列的表示法有效
df1.select("ename", "hiredate", "sal"+100).show
df1.select("ename", "hiredate", "sal+100").show
// 这样写才符合语法
df1.select($"ename", $"hiredate", $"sal"+100).show
df1.select('ename, 'hiredate, 'sal+100).show
// 可使用expr表达式(expr里面只能使用引号)
df1.select(expr("comm+100"), expr("sal+100"),
expr("ename")).show
df1.selectExpr("ename as name").show
df1.selectExpr("power(sal, 2)", "sal").show
df1.selectExpr("round(sal, -3) as newsal", "sal",
"ename").show
// drop、withColumn、 withColumnRenamed、casting
// drop 删除一个或多个列,得到新的DF
df1.drop("mgr")
df1.drop("empno", "mgr")
// withColumn,修改列值
val df2 = df1.withColumn("sal", $"sal"+1000)
df2.show
// withColumnRenamed,更改列名
df1.withColumnRenamed("sal", "newsal")
// 备注:drop、withColumn、withColumnRenamed返回的是DF
// cast,类型转换
df1.selectExpr("cast(empno as string)").printSchema
import org.apache.spark.sql.types._
df1.select('empno.cast(StringType)).printSchemawhere 相关的
where=filter
// where操作
df1.filter("sal>1000").show
df1.filter("sal>1000 and job=='MANAGER'").show
// filter操作
df1.where("sal>1000").show
df1.where("sal>1000 and job=='MANAGER'").showgroupBy相关的
groupBy、agg、max、min、avg、sum、count(后面5个为内置函数)df1.groupBy("Job").sum("sal").show
df1.groupBy("Job").max("sal").show
df1.groupBy("Job").min("sal").show
df1.groupBy("Job").avg("sal").show
df1.groupBy("Job").count.show
// 类似having子句
df1.groupBy("Job").avg("sal").where("avg(sal) > 2000").show
df1.groupBy("Job").avg("sal").where($"avg(sal)" > 2000).show
// agg
df1.groupBy("Job").agg("sal"->"max", "sal"->"min", "sal"->"avg", "sal"->"sum", "sal"->"count").show
df1.groupBy("deptno").agg("sal"->"max", "sal"->"min", "sal"->"avg", "sal"->"sum", "sal"->"count").show
// 这种方式更好理解
df1.groupBy("Job").agg(max("sal"), min("sal"), avg("sal"),
sum("sal"), count("sal")).show
// 给列取别名
df1.groupBy("Job").agg(max("sal"), min("sal"), avg("sal"),
sum("sal"), count("sal")).withColumnRenamed("min(sal)",
"min1").show
// 给列取别名,最简便
df1.groupBy("Job").agg(max("sal").as("max1"),
min("sal").as("min2"), avg("sal").as("avg3"),
sum("sal").as("sum4"), count("sal").as("count5")).showorderBy相关的
// orderBy
df1.orderBy("sal").show
df1.orderBy($"sal").show
df1.orderBy($"sal".asc).show
// 降序
df1.orderBy(-$"sal").show
df1.orderBy('sal).show
df1.orderBy(col("sal")).show
df1.orderBy(df1("sal")).show
df1.orderBy($"sal".desc).show
df1.orderBy(-'sal).show
df1.orderBy(-'deptno, -'sal).show
// sort,以下语句等价
df1.sort("sal").show
df1.sort($"sal").show
df1.sort($"sal".asc).show
df1.sort('sal).show
df1.sort(col("sal")).show
df1.sort(df1("sal")).show
df1.sort($"sal".desc).show
df1.sort(-'sal).show
df1.sort(-'deptno, -'sal).showjoin相关的
// 1、笛卡尔积
df1.crossJoin(df1).count
// 2、等值连接(单字段)(连接字段empno,仅显示了一次)
df1.join(df1, "empno").count
// 3、等值连接(多字段)(连接字段empno、ename,仅显示了一次)
df1.join(df1, Seq("empno", "ename")).show// 1、笛卡尔积
df1.crossJoin(df1).count
// 2、等值连接(单字段)(连接字段empno,仅显示了一次)
df1.join(df1, "empno").count
// 3、等值连接(多字段)(连接字段empno、ename,仅显示了一次)
df1.join(df1, Seq("empno", "ename")).show
// 备注:不能使用双引号,而且这里是 ===
ds1.join(ds2, $"name"===$"sname").show
ds1.join(ds2, 'name==='sname).show
ds1.join(ds2, ds1("name")===ds2("sname")).show
ds1.join(ds2, ds1("sname")===ds2("sname"), "inner").show
// 多种连接方式
ds1.join(ds2, $"name"===$"sname").show
ds1.join(ds2, $"name"===$"sname", "inner").show
ds1.join(ds2, $"name"===$"sname", "left").show
ds1.join(ds2, $"name"===$"sname", "left_outer").show
ds1.join(ds2, $"name"===$"sname", "right").show
ds1.join(ds2, $"name"===$"sname", "right_outer").show
ds1.join(ds2, $"name"===$"sname", "outer").show
ds1.join(ds2, $"name"===$"sname", "full").show
ds1.join(ds2, $"name"===$"sname", "full_outer").show便于记忆和使用,统一写成下述格式
ds1.join(ds2, ds1(“sname”)===ds2(“sname”), “inner”).show
集合相关的
union==unionAll(过期)、intersect、except
// union、unionAll、intersect、except。集合的交、并、差
val ds3 = ds1.select("name")
val ds4 = ds2.select("sname")
// union 求并集,不去重
ds3.union(ds4).show
// unionAll、union 等价;unionAll过期方法,不建议使用
ds3.unionAll(ds4).show
// intersect 求交
ds3.intersect(ds4).show
// except 求差
ds3.except(ds4).show空值处理
na.fill、na.drop
// NaN (Not a Number)
math.sqrt(-1.0)
math.sqrt(-1.0).isNaN()
df1.show
// 删除所有列的空值和NaN
df1.na.drop.show
// 删除某列的空值和NaN
df1.na.drop(Array("mgr")).show
// 对全部列填充;对指定单列填充;对指定多列填充
df1.na.fill(1000).show
df1.na.fill(1000, Array("comm")).show
df1.na.fill(Map("mgr"->2000, "comm"->1000)).show
// 对指定的值进行替换
df1.na.replace("comm" :: "deptno" :: Nil, Map(0 -> 100, 10 ->
100)).show
// 查询空值列或非空值列。isNull、isNotNull为内置函数
df1.filter("comm is null").show
df1.filter($"comm".isNull).show
df1.filter(col("comm").isNull).show
df1.filter("comm is not null").show
df1.filter(col("comm").isNotNull).show内建数据源详解
数据源之通用操作load和save操作
load:数据加载进spark
save:数据从spark写出到文件中
val df = spark.read.load("users.parquet")
df.select("name", "age").write.save("namesAndAges.parquet")Spark SQL对于save操作,提供了不同的save mode。主要用来处理,当目标位置,已经有数据时,应该如何处理。而且save操作并不会执行锁操作,并且不是原子的,因此是有一定风险出现脏数据的
| Save Mode | 意义 |
| SaveMode.ErrorIfExists (默认) | 如果目标位置已经存在数据,那么抛出一个异常 |
| SaveMode.Append | 如果目标位置已经存在数据,那么将数据追加进去 |
| SaveMode.Overwrite | 如果目标位置已经存在数据,那么就将已经存在的数据删除,用新数据进行覆盖 |
| SaveMode.Ignore | 如果目标位置已经存在数据,那么就忽略,不做任何操作。 |
SparkSQL内建支持的数据源包括:Parquet、JSON、CSV、Avro、Images、
BinaryFiles(Spark 3.0)。其中Parquet是默认的数据源
计算引擎是Spark的话,推荐选择Parquet
查询引擎主要是Presto的话,Presto对ORC文件读取做了特定的优化,这中情况下,推荐使用ORC会更好
Spark on hive 与 Hive on Spark 的区别
Spark on hive:
Spark通过Spark-SQL使用hive 语句,操作hive,底层运行的还是 spark rddHive on Spark:
是把hive查询从mapreduce 的mr (Hadoop计算引擎)操作替换为spark rdd(spark 执行引擎) 操作. 相对于spark on hive,这个要实现起来则麻烦很多, 必须重新编译spark和导入jar包,不过目前大部分使用的是spark on hiveSpark 提供了两种写入hive的模式saveAsTable, insertInto
saveAstable
当schema存在时依赖以下几种存储模式:
append :追加数据到已存在的表
overwrite:覆盖已存在的数据
error or errorifexsists:数据已存在则抛出异常(默认)
ignore:数据/分区已存在忽略,不会插入数据与saveAsTable 最大的区别就是要求表必须存在否则插入会报错,并且dateframe的schema与目标表的schema字段个数要保持一致
Spark SQL 常用函数
// 日期格式化
spark.sql("select to_date('20220401','yyyyMMdd')").show()
//date_format(timestamp, fmt) - Converts timestamp to a value of string in the format specified by the date format fmt.
spark.sql("SELECT date_format('2016-04-08', 'y')")
// date_add(start_date, num_days) - Returns the date that is num_days after start_date.
spark.sql("SELECT date_add('2016-07-30', 1)")
// date_sub date_sub(start_date, num_days) - Returns the date that is num_days before start_date.
spark.sql("SELECT date_sub('2016-07-30', 1)")
// datediff(endDate, startDate) - Returns the number of days from startDate to endDate.
spark.sql("SELECT datediff('2009-07-31', '2009-07-30')")
// from_unixtime(unix_time, format) - Returns unix_time in the specified format.
spark.sql("SELECT from_unixtime(0, 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')")
// from_utc_timestamp(timestamp, timezone) - Given a timestamp like '2017-07-14 02:40:00.0', interprets it as a time in UTC, and renders that time as a timestamp in the given time zone. For example, 'GMT+1' would yield '2017-07-14 03:40:00.0'.
spark.sql(" SELECT from_utc_timestamp('2016-08-31', 'Asia/Seoul');")
// last_day(date) - Returns the last day of the month which the date belongs to.
spark.sql("SELECT last_day('2009-01-12')")
// explode(expr) - Separates the elements of array expr into multiple rows, or the elements of map expr into multiple rows and columns.
spark.sql("SELECT explode(array(10, 20))")
// from_json(jsonStr, schema[, options]) - Returns a struct value with the given jsonStr and schema.
spark.sql("SELECT from_json('{\"a\":1, \"b\":0.8}', 'a INT, b DOUBLE')")
spark.sql("SELECT from_json('{\"time\":\"26/08/2015\"}', 'time Timestamp', map('timestampFormat', 'dd/MM/yyyy'))")
//get_json_object(json_txt, path) - Extracts a json object from path.
spark.sql("SELECT get_json_object('{\"a\":\"b\"}', '$.a')")
//json_tuple
spark.sql("SELECT json_tuple('{\"a\":1, \"b\":2}', 'a', 'b');")
//to_json(expr[, options]) - Returns a json string with a given struct value
spark.sql("select to_json(named_struct('a', 1, 'b', 2))")
spark.sql("select to_json(named_struct('time', to_timestamp('2015-08-26', 'yyyy-MM-dd')), map('timestampFormat', 'dd/MM/yyyy'))")
spark.sql("select to_json(array(named_struct('a', 1, 'b', 2))")
spark.sql("select to_json(map('a', named_struct('b', 1)))")
spark.sql("SELECT to_json(map(named_struct('a', 1),named_struct('b', 2)))")
spark.sql("SELECT to_json(map('a', 1))")
spark.sql("SELECT to_json(array((map('a', 1))))")
// 数组 array(expr, ...) - 返回给定值组成的数组。
spark.sql("select array(1,3,4)")
// array_contains(array, value) - 如果数组包含了 value,则返回 true。
spark.sql("select array_contains(array(1,3,4),1)")
// size size(expr) - Returns the size of an array or a map. Returns -1 if null.
spark.sql("SELECT size(array('b', 'd', 'c', 'a'))")
// sort_array(array[, ascendingOrder]) - Sorts the input array in ascending or descending order according to the natural ordering of the array elements.
spark.sql("SELECT sort_array(array('b', 'd', 'c', 'a'), true)")
// collect_list(expr) - 收集并返回非唯一元素列表。
spark.sql("select a,collect_list(b) from table group a ")
// collect_set(expr) - 收集并返回唯一元素列表。
spark.sql("select a,collect_set(b) from table group a ")
// map
//map(key0, value0, key1, value1, ...) - Creates a map with the given key/value pairs.
spark.sql("SELECT map(1.0, '2', 3.0, '4')")
// map_keys(map) - Returns an unordered array containing the keys of the map.
spark.sql("SELECT map_keys(map(1, 'a', 2, 'b'))")
// map_values(map) - Returns an unordered array containing the values of the map.
spark.sql("SELECT map_values(map(1, 'a', 2, 'b'))")
// struct
// struct(col1, col2, col3, ...) - Creates a struct with the given field values.
spark.sql("select struct(1 as a, 2 as b) s")
// coalesce(expr1, expr2, ...) - 返回第一个非空参数(如果存在)。 否则,返回 null。
spark.sql("SELECT coalesce(NULL, 1, NULL)")sparksql开窗函数
一般情况下窗口函数不用 DSL 处理,直接用SQL更方便
import org.apache.spark.sql.expressions.Window
val w1 = Window.partitionBy("cookieid").orderBy("createtime")
val w2 = Window.partitionBy("cookieid").orderBy("pv")
val w3 = w1.rowsBetween(Window.unboundedPreceding, Window.currentRow)
val w4 = w1.rowsBetween(-1, 1)
// 聚组函数【用分析函数的数据集】
df.select($"cookieid", $"pv", sum("pv").over(w1).alias("pv1")).show
df.select($"cookieid", $"pv", sum("pv").over(w3).alias("pv1")).show
df.select($"cookieid", $"pv", sum("pv").over(w4).as("pv1")).show
df.select($"cookieid", $"pv", rank().over(w2).alias("rank")).show
df.select($"cookieid", $"pv", dense_rank().over(w2).alias("denserank")).show
df.select($"cookieid", $"pv", row_number().over(w2).alias("rownumber")).show
// lag、lead
df.select($"cookieid", $"pv", lag("pv", 2).over(w2).alias("rownumber")).show
df.select($"cookieid", $"pv", lag("pv", -2).over(w2).alias("rownumber")).show